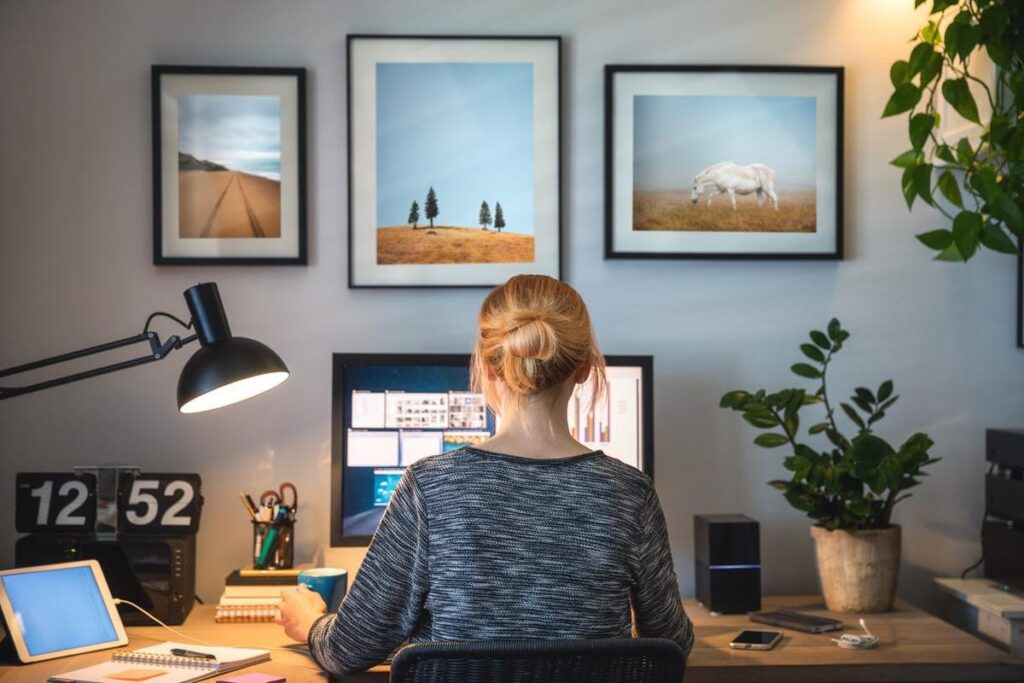
Remote work, often called telecommuting or teleworking, refers to a work arrangement where employees perform their job duties outside a traditional office environment. This is typically facilitated through digital communication and collaboration tools, allowing employees to work from home, coworking spaces, or any location of their choice.
Remote work has evolved significantly, becoming a defining trend in the modern workplace, especially following global shifts caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Here’s a detailed look at the future of remote work, exploring its pros and cons:
Pros of Remote Work
1. Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
Employees can tailor their work schedules to their personal lives, enhancing satisfaction and reducing stress. Flexibility accommodates diverse lifestyles and family commitments, leading to higher job satisfaction.
2. Cost Savings
For employees: Reduced expenses on commuting, eating out, and work attire. For employers: Lower overhead costs for office spaces and utilities.
3. Increased Productivity
Many workers report being more productive in a personalized, distraction-free environment. Fewer workplace distractions and reduced time spent commuting contribute to efficiency.
4. Access to a Broader Talent Pool
Companies can hire talent globally, leading to a diverse and skilled workforce. Employees are not limited by geographic constraints, opening opportunities worldwide.
5. Environmental Benefits
Decreased commuting reduces carbon footprints and urban congestion. Less office energy consumption aligns with sustainability goals.
6. Health Benefits
Flexible schedules allow for better mental health management. Less exposure to illnesses in crowded office settings.
Cons of Remote Work
- Isolation and Loneliness
- Lack of in-person interaction can lead to feelings of detachment and loneliness.
- Collaboration and team spirit may be harder to foster in virtual settings.
2. Work-Life Boundary Challenges
- Blurred lines between work and personal life can lead to overworking and burnout.
- The lack of a structured office environment might make it hard to “log off.”
3. Reduced Collaboration and Innovation
- Spontaneous brainstorming and collaborative problem-solving are less organic in remote settings.
- Dependence on digital tools for collaboration may not replicate the dynamics of in-person meetings.
4. Technological Dependence and Barriers
- Reliable internet and technology are critical but not universally accessible.
- Cybersecurity risks increase with dispersed workforces using varying networks and devices.
5. Performance Monitoring and Accountability
- Managers may struggle with assessing productivity and maintaining team accountability.
- Employees might feel micromanaged if invasive tracking technologies are employed.
Unequal Opportunities
-
- Remote workers might miss out on informal office networking and career growth opportunities.
- Promotions and recognitions may skew toward in-office employees in hybrid setups.

Future Trends and Considerations
1. Hybrid Work Models
Combining in-office and remote work could offer the best of both worlds. Flexible arrangements cater to individual preferences and business needs.
2. Advanced Collaboration Tools
Technologies like VR, AR, and AI-powered platforms will enhance virtual interactions. Seamless integration across devices will reduce tech barriers.
3. Employee Well-being Programs
Companies will invest more in mental health resources and virtual team-building activities. Policies promoting work-life balance will become a priority.
4. Decentralized Offices
Satellite offices or coworking spaces might emerge as alternatives to traditional headquarters. Regional hubs can provide face-to-face engagement without full relocation.
5. Policy and Legal Implications
Governments and organizations will need to address remote work laws, tax policies, and labor rights. Standardized policies for remote work agreements will become the norm.
Conclusion
The future of remote work lies in balancing its advantages while addressing its challenges. With thoughtful strategies, businesses and individuals can thrive in a flexible, remote-first environment. Ultimately, success depends on adapting to technological advancements, fostering meaningful connections, and ensuring equitable opportunities for all workers.
The future of remote work will revolve around hybrid models, combining flexibility with in-office collaboration. Technology like AI and virtual tools will enhance communication, making remote setups more seamless. Companies will focus on performance-based outcomes, prioritizing results over hours worked. While flexibility boosts productivity and work-life balance, challenges like isolation and equity in opportunities will need proactive solutions. Organizations that adapt to these dynamics and prioritize employee well-being will thrive. Remote work is set to become a lasting cornerstone of the modern workplace.